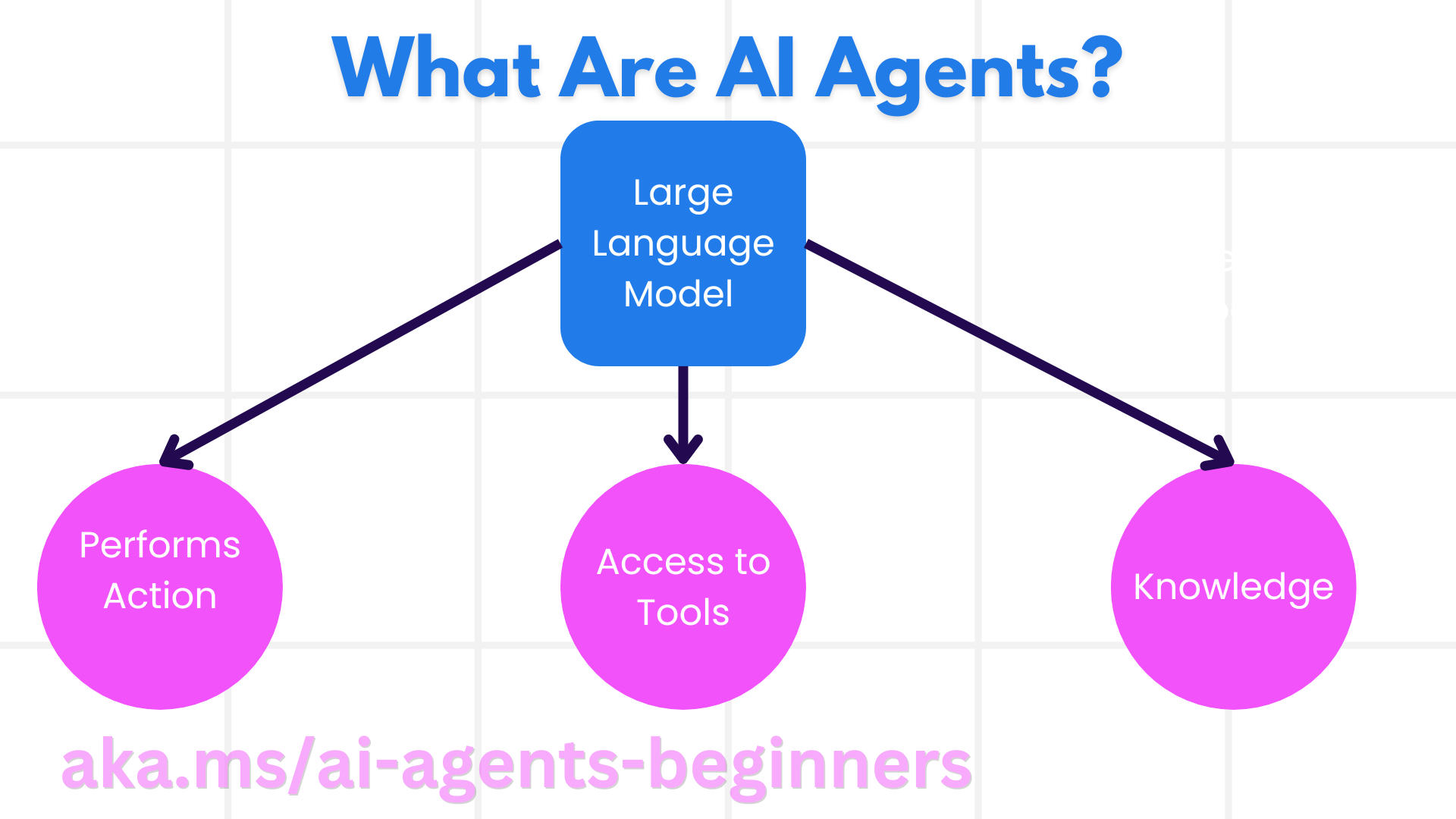
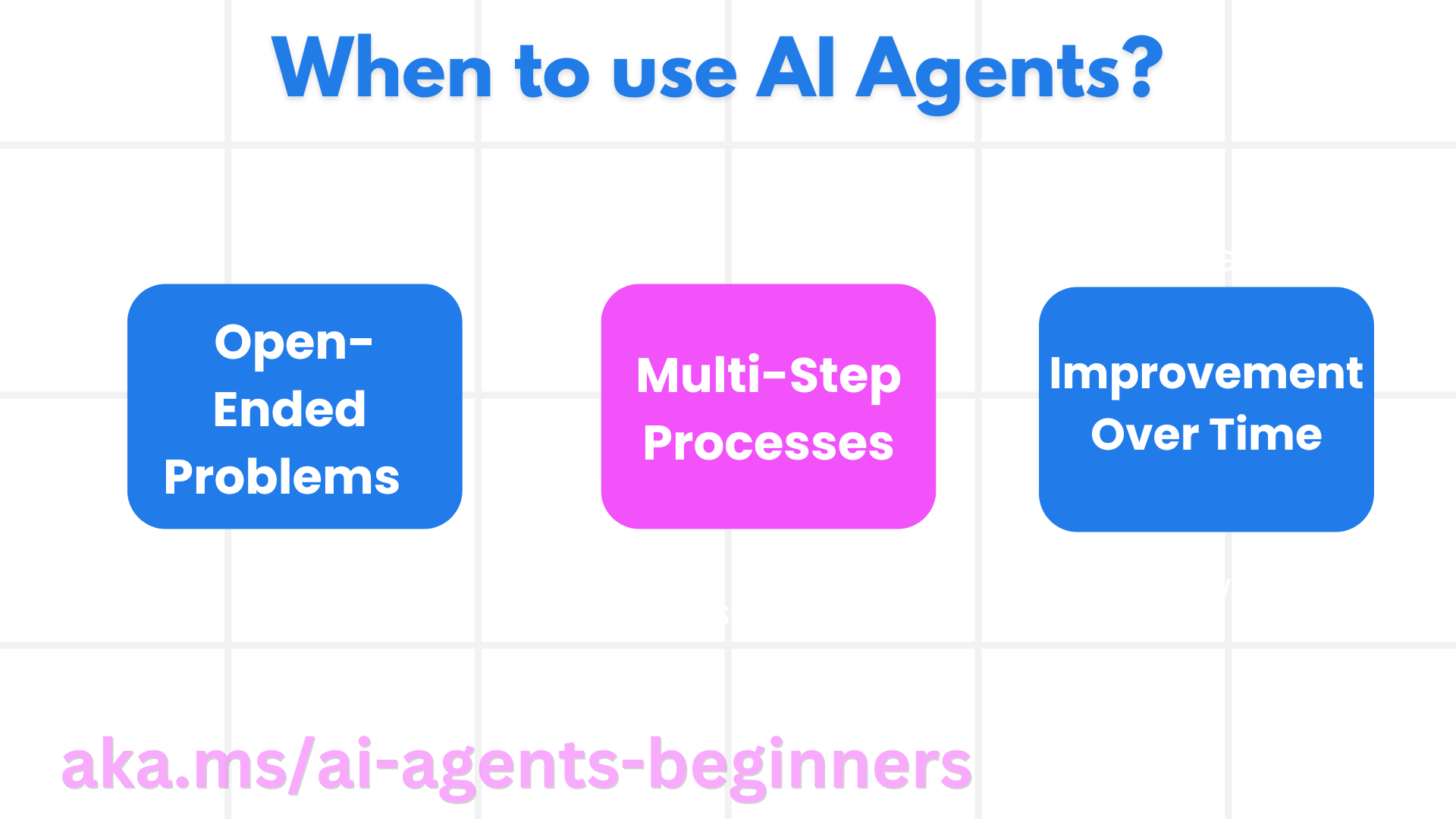
Information
Welcome to the “AI Agents for Beginners” course! This course provides fundamental knowledge and applied samples for building AI Agents. Join the Azure AI Discord Community to meet other learners and AI Agent Builders and ask any questions you have about this course. To start this course, we begin by getting a better understanding of what AI Agents are and how we can use them in the applications and workflows we build. This lesson covers: After completing this lesson, you should be able to: AI Agents are systems that enable Large Language Models(LLMs) to perform actions by extending their capabilities by giving LLMs access to tools and knowledge. Let’s break this definition into smaller parts: Large Language Models - The concept of agents existed before the creation of LLMs. The advantage of building AI Agents with LLMs is their ability to interpret human language and data. This ability enables LLMs to interpret environmental information and define a plan to change the environment. Perform Actions - Outside of AI Agent systems, LLMs are limited to situations where the action is generating content or information based on a user’s prompt. Inside AI Agent systems, LLMs can accomplish tasks by interpreting the user’s request and using tools that are available in their environment. Access To Tools - What tools the LLM has access to is defined by 1) the environment it’s operating in and 2) the developer of the AI Agent. For our travel agent example, the agent’s tools are limited by the operations available in the booking system, and/or the developer can limit the agent’s tool access to flights. Knowledge - Outside of the information provided by the environment, AI Agents can also retrieve knowledge from other systems, services, tools, and even other agents. In the travel agent example, this knowledge could be the information on the user’s travel preferences located in a customer database. Now that we have a general definition of AI Agents, let us look at some specific agent types and how they would be applied to a travel booking AI agent. In the earlier section, we used the Travel Agent use-case to explain how the different types of agents can be used in different scenarios of travel booking. We will continue to use this application throughout the course. Let’s look at the types of use cases that AI Agents are best used for: We cover more considerations of using AI Agents in the Building Trustworthy AI Agents lesson. The first step in designing an AI Agent system is to define the tools, actions, and behaviors. In this course, we focus on using the Azure AI Agent Service to define our Agents. It offers features like: Communication with LLMs is through prompts. Given the semi-autonomous nature of AI Agents, it isn’t always possible or required to manually reprompt the LLM after a change in the environment. We use Agentic Patterns that allow us to prompt the LLM over multiple steps in a more scalable way. This course is divided into some of the current popular Agentic patterns. Agentic Frameworks allow developers to implement agentic patterns through code. These frameworks offer templates, plugins, and tools for better AI Agent collaboration. These benefits provide abilities for better observability and troubleshooting of AI Agent systems. In this course, we will explore the research-driven AutoGen framework and the production ready Agent framework from Semantic Kernel.